Bees and wasps are fascinating creatures that often capture our curiosity and, at times, concern. While they may appear similar at first glance, there are important differences between carpenter bees and wasps that set them apart. Understanding these distinctions can help us identify and coexist with these important pollinators.
Let’s explore the similarities and differences between carpenter bees and wasps, their nesting habits, the potential damage they can cause, and how to handle their presence. Whether you’re dealing with a carpenter bee infestation or concerned about wasp stings, this guide will provide you with the necessary information to navigate these buzzing creatures.
Key Takeaways:
- Carpenter bees and wasps may look similar but have distinct differences in body shape and appearance.
- Carpenter bees have rounder bodies, visible hair, and flat, hairy legs, while wasps have narrower bodies, small invisible hairs, and cylindrical, hairless legs.
- Bees have barbed stingers and can only sting once, while wasps have smooth stingers and can sting multiple times.
- Both bees and wasps play a role in pollination, but wasps can also be a nuisance and may require removal if they pose a threat to homes or businesses.
- Proper pest control measures, prevention strategies, and the conservation of bee habitats are crucial for maintaining a healthy ecosystem and sustainable future.
Identifying Bees and Wasps by Appearance
When it comes to distinguishing between bees and wasps, their appearance is a key factor. Bees have rounder bodies, with the head, thorax, and abdomen appearing to meld together. They are covered in visible hairs, giving them a furry and textured appearance. On the other hand, wasps have narrower bodies with thin waists, and their bodies are segmented. They have small, invisible hairs that make them appear shiny.
Another distinguishing feature is their legs. Bees have flat, hairy legs that are adapted for carrying pollen. In contrast, wasps have cylindrical, hairless legs. You may even notice that when in flight, bees keep their legs tucked away, while wasps let their legs hang down.
To summarize, bees can be identified by their rounder bodies, visible hair, and flat, hairy legs, while wasps have narrower bodies, small invisible hairs, and cylindrical, hairless legs. These distinct physical characteristics can help you differentiate between these two insects.
Differences in Stings and Stingers
When it comes to stings and stingers, bees and wasps have significant differences. Bees have barbed stingers that get stuck in the victim’s skin, which ultimately kills the bee. On the other hand, wasps have smooth stingers and do not lose them when they sting. This allows them to sting multiple times, increasing the potential danger they pose. So, if you see a stinger at the site of a sting, it’s likely from a bee, while the absence of a stinger suggests a wasp sting.
The difference in stingers also affects the aggressive behavior of bees and wasps. Bees are generally less aggressive and are more focused on foraging for pollen and nectar. They will only sting if they feel threatened or provoked. Wasps, however, are typically more aggressive and more likely to sting. They can become defensive and attack if their nest or territory is disturbed.
It’s important to note that both bee and wasp stings can cause pain and allergic reactions in some individuals. For those with allergies, a sting can be life-threatening. If you have been stung and experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness, seek medical attention immediately.
Differences in Stings and Stingers
| Bees | Wasps | |
|---|---|---|
| Stinger Type | Barbed stinger | Smooth stinger |
| Multiple Stings | No | Yes |
| Aggressiveness | Less aggressive, sting if provoked | More aggressive, more likely to sting |
“The difference in stingers also affects the aggressive behavior of bees and wasps. Bees are generally less aggressive and are more focused on foraging for pollen and nectar. They will only sting if they feel threatened or provoked. Wasps, however, are typically more aggressive and more likely to sting.”
Understanding the differences in stings and stingers between bees and wasps can help you identify the source of a sting and take appropriate action. If you have a nest on your property or are dealing with a significant infestation, it’s best to seek professional help to safely remove the nests and address the issue. Prevention is also key in minimizing the risk of bee and wasp stings. Keep food and garbage properly sealed, seal any cracks or openings in your home, and remove potential nesting sites.
Common Types of Wasps (Hornets, Mud Daubers, Paper Wasps, Yellow Jackets)
Wasps are a diverse group of insects, with several common types that are encountered in various habitats. Understanding the characteristics and behaviors of these different wasp species can help in their identification and appropriate management. Here are some of the most common types of wasps:
Hornets
Hornets are a type of wasp known for their large size and aggressive behavior. The European hornet and bald-faced hornet are the two hornet species with established populations in the United States. Hornets have slightly thicker waists compared to other wasp species.
Mud Daubers
Mud daubers are solitary wasps that build nests out of mud. They are typically black, metallic blue, or black and yellow in color. Mud daubers construct their nests in various locations such as eaves, ceilings, attics, and sheds. They are not typically aggressive and pose minimal risk to humans.
Paper Wasps
Paper wasps are social wasps that build distinct umbrella-shaped nests. These nests are constructed from a paper-like material made by chewing wood and plant fibers. Paper wasps are often found in high areas such as attics, eaves, and tree branches. They are usually not aggressive unless their nests are disturbed.
Yellow Jackets
Yellow jackets are small wasps with yellow and black bands on their abdomens. They are social insects that build nests both underground and in protected areas such as attics and wall voids. Yellow jackets can be aggressive and are known for their painful stings. They are a common nuisance around picnics and outdoor activities.
| Common Types of Wasps | Description | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Hornets | A type of wasp with slightly thicker waists | Aggressive |
| Mud Daubers | Solitary wasps that build nests out of mud | Non-aggressive |
| Paper Wasps | Social wasps that build umbrella-shaped nests | Non-aggressive unless disturbed |
| Yellow Jackets | Small wasps with yellow and black bands on abdomen | Aggressive |
It is important to note that while wasps can be beneficial for controlling other pests, their aggressive behavior and painful stings can pose risks in certain situations. If you are facing a wasp infestation or concerned about their presence, it is advisable to seek professional help for safe and effective removal.
Common Types of Bees (Bumblebees, Carpenter Bees, Honey Bees, Mining Bees, Sweat Bees, Mason Bees)
Bees are a diverse group of insects that play a crucial role in pollination. They come in various species, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. Here, we will explore some of the most common types of bees:
Bumblebees
Bumblebees are larger than honeybees and are known for their fuzzy appearance. They have black bodies covered with dense yellow and black hairs. Bumblebees are important pollinators of native wildflowers and certain agricultural crops. They build their nests in the ground and are known for their gentle nature.
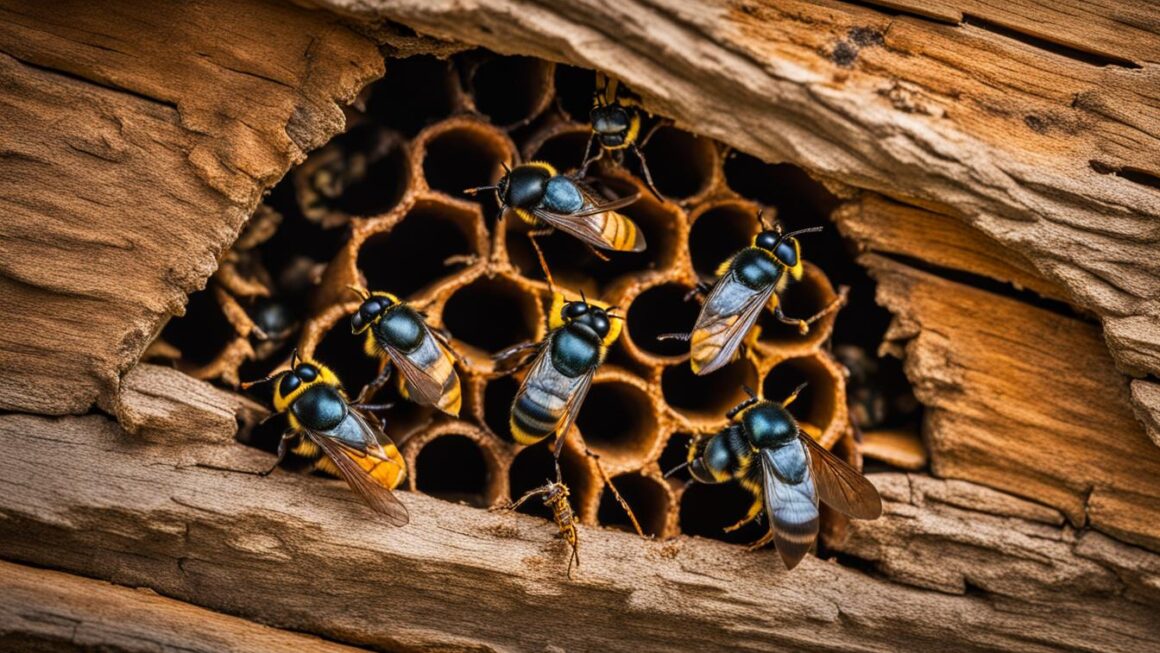
Carpenter Bees
Carpenter bees are known for their ability to bore tunnels into wood. They have shiny, hairless abdomens and are often mistaken for bumblebees. While they can cause damage to structures, they also play an important role in pollination. Carpenter bees can often be found around wooden structures such as decks, eaves, and fences.
Honey Bees
Honey bees are perhaps the most well-known type of bee. They are golden brown with black abdominal stripes and are commonly kept in artificial hives by beekeepers. Honey bees are important agricultural pollinators and are responsible for producing honey. They live in large colonies and are known for their complex social structure.
Mining Bees
Mining bees are solitary bees that dig nests underground. They are often mistaken for bumblebees due to their similar appearance. Mining bees are gentle and rarely sting unless provoked. They play a role in pollinating a variety of flowers and are important contributors to ecosystem health.
Sweat Bees
Sweat bees are small bees that are attracted to human sweat. They are often metallic green, blue, or black in color. Sweat bees can build nests underground or in softwood. While they may occasionally sting if threatened, their stings are usually mild. Sweat bees are important pollinators of a wide range of plants.
Mason Bees
Mason bees are small, fast-flying bees with metallic colors. They carry pollen on the underside of their abdomens and are important pollinators of spring-flowering fruit and nut trees. Mason bees are solitary bees that build nests in existing cavities, such as hollow plant stems or holes in wood.
Each type of bee has its own unique characteristics and role in the ecosystem. Understanding these differences is essential for appreciating the diversity and importance of bees in our environment.
| Bee Type | Appearance | Nesting Habit | Pollination Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bumblebees | Large, fuzzy, black bodies with dense yellow and black hairs | Ground nests | Important pollinators of native wildflowers and crops |
| Carpenter Bees | Shiny, hairless abdomens | Bore tunnels into wood | Contribute to pollination, can cause structural damage |
| Honey Bees | Golden brown with black abdominal stripes | Live in large colonies, often in artificial hives | Key agricultural pollinators, produce honey |
| Mining Bees | Similar appearance to bumblebees | Dig nests underground | Pollinate a variety of flowers, contribute to ecosystem health |
| Sweat Bees | Metallic green, blue, or black bodies | Build nests underground or in softwood | Important pollinators attracted to human sweat |
| Mason Bees | Small, fast-flying bees with metallic colors | Build nests in existing cavities | Key pollinators of spring-flowering fruit and nut trees |
Behavior and Habitat of Bees and Wasps
Bees and wasps exhibit different behavior and have distinct habitats that contribute to their roles as pollinators and potential pests. Bees, known for their important role in pollination, are generally non-aggressive unless provoked. They primarily focus on foraging for pollen and nectar from flowers, contributing to the fertilization of plants and the production of fruits and seeds. Bees live in various nest structures, including ground nests, tree cavities, attics, and eaves.
Wasps, on the other hand, can be more aggressive and may sting if threatened. While they also play a role in pollination, their nesting habits can make them a nuisance. Wasps build their nests in high places, such as attics, sheds, and trees, utilizing their saliva and wood fibers to create paper-like structures. These nests can pose risks to homes and businesses, potentially causing damage to structures.
Table:
| Behavior | Bees | Wasps |
|---|---|---|
| Aggressiveness | Non-aggressive, unless provoked | Can be aggressive, especially when threatened |
| Pollination | Mainly focused on foraging for pollen and nectar, contributing to plant fertilization | Also play a role in pollination, but can be a nuisance |
| Nesting Habits | Various nest structures, including ground nests, tree cavities, attics, and eaves | Build nests in high places, such as attics, sheds, and trees, utilizing saliva and wood fibers |
It’s important to understand the behavior and nesting preferences of bees and wasps to effectively manage their presence. While bees should be conserved due to their declining populations and ecological significance as pollinators, wasps may require professional removal if they pose a threat or cause damage. Coexistence with these insects can be achieved through proper pest control measures, prevention strategies, and the conservation of their habitats.
Potential Damage and Risks Associated with Bees and Wasps
Bees and wasps can cause various types of damage and pose risks to both humans and structures. It is important to be aware of these potential dangers and take appropriate measures to protect yourself and your property.
Damage caused by bees:
- Structural damage: Carpenter bees can bore tunnels into wood, weakening wooden structures such as decks, fences, and even the wooden components of homes. Their activity can lead to costly repairs and compromises the structural integrity of the affected areas.
- Garden damage: Bees, particularly mining bees, can cause damage to lawns and gardens by creating unsightly nesting burrows. These burrows can disrupt the growth of grass and plants, affecting the overall aesthetics of outdoor spaces.
Damage caused by wasps:
- Structural damage: Wasps can build nests in and around homes, sheds, and other structures. Their nest-building activities can result in damage to the building materials, such as wood, and may require professional assistance for safe removal and repair.
- Stinging: The sting of a wasp can be painful and, for some individuals, can cause severe allergic reactions. This can be particularly dangerous if a person is stung multiple times or is highly sensitive to the venom. It is important to exercise caution when dealing with wasp nests or when in outdoor areas where wasps are present.
To mitigate the potential damage and risks associated with bees and wasps, it is advisable to seek professional assistance for nest removal and pest control. Attempting to remove nests or control infestations without proper knowledge and equipment can lead to accidental stings and further damage to structures.
| Type of Damage | Caused by Bees | Caused by Wasps |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Damage | Carpenter bees bore tunnels into wood, weakening structures. | Wasps build nests in and around homes, potentially causing damage to structures. |
| Garden Damage | Mining bees create unsightly nesting burrows that can disrupt the growth of grass and plants. | N/A |
| Stinging | Bee stings can cause pain and allergic reactions in some individuals. | Wasp stings can be painful and may cause severe allergic reactions. |
It is crucial to exercise caution and prioritize safety when dealing with bees and wasps. Consulting with professionals in pest control and bee/wasp removal is recommended to ensure the effective and safe mitigation of potential risks and damage.
Removing Bees and Wasps
When dealing with bee and wasp infestations, it is crucial to prioritize safety and seek professional help to ensure a proper removal process. While DIY methods can be effective for smaller infestations, larger nests or colonies should be handled by experienced pest control experts to avoid any potential risks. Professional removal not only guarantees the safety of those involved but also ensures the effective relocation and management of these insects.
Professional pest control services employ trained technicians who are knowledgeable about the behavior and habits of bees and wasps. They have the necessary equipment and expertise to safely remove nests from various locations, including homes, businesses, and other structures. By hiring professionals, you can minimize the chances of getting stung and protect your property from potential damage.
In situations where the nest location poses a threat, professional removal is especially crucial. Bees and wasps can build nests in inconvenient areas, such as within the walls, attics, or near doorways. Attempting to remove these nests without proper knowledge and tools can lead to further damage and potential injuries.
| DIY Methods | Professional Removal |
|---|---|
|
|

Remember, when it comes to removing bees and wasps, it’s best to leave it to the professionals. Their expertise and experience ensure a safe and efficient removal process, protecting both you and the insects involved. By relying on professional pest control services, you can effectively manage bee and wasp infestations and safeguard your property.
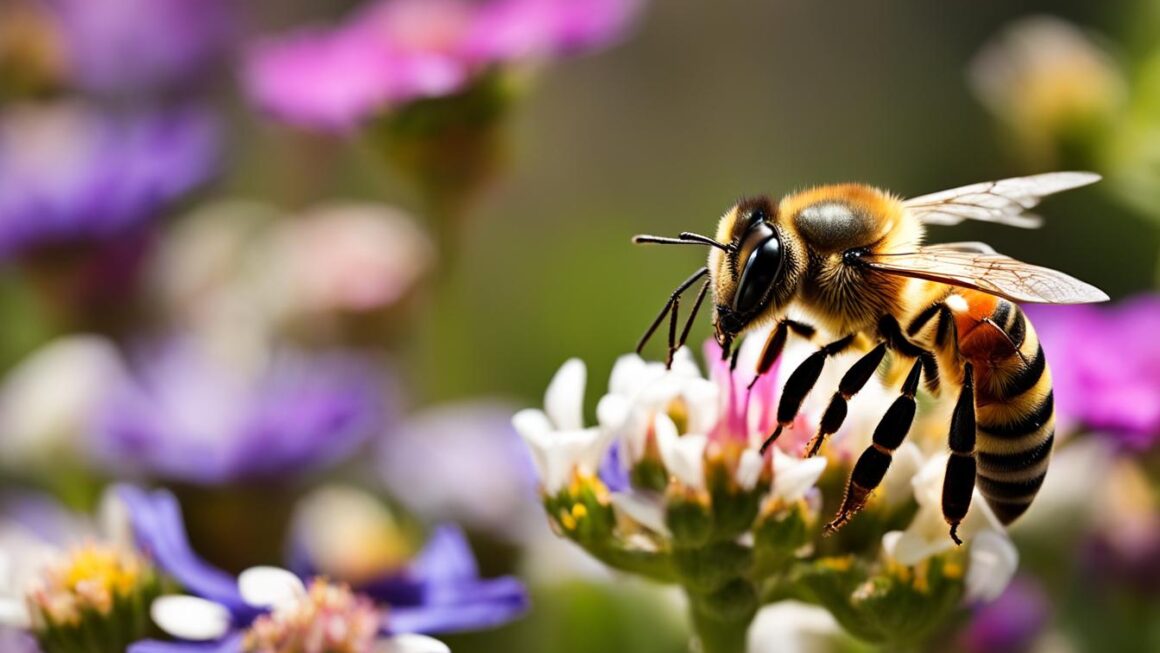
Importance of Bees and Wasps in Pollination
Bees and wasps play a crucial role in the process of pollination, which is vital for the reproduction and survival of many plant species. Through their foraging activities, they transfer pollen from the male parts of flowers to the female parts, enabling plants to produce fruits and seeds. This process ensures genetic diversity, allowing plants to adapt to changing environments and maintain healthy populations.
Bees, with their fuzzy bodies and specialized structures like hairy legs, are particularly effective pollinators. As they collect nectar and pollen from flowers, these tiny particles stick to their bodies and are transferred from one flower to another as they move around. This cross-pollination facilitates the fertilization of plants, promoting genetic variation and enhancing the quality of fruits, vegetables, and other crops.
Wasps also contribute to the pollination process, although to a lesser extent compared to bees. While bees are mostly attracted to flowers with nectar, wasps are often drawn to flowers for other reasons, such as hunting for insects or feeding on ripe or decaying fruits. In the process, they inadvertently carry pollen from flower to flower, aiding in their pollination. Despite their reputation as aggressive insects, it’s important to recognize the valuable role wasps play in ecosystems.
The Role of Bees and Wasps in Agriculture
The importance of bees and wasps in pollination extends beyond natural ecosystems to agricultural systems. Farmers rely on these insects to pollinate crops such as apples, almonds, avocados, berries, and many others. Without the pollination services provided by bees and wasps, the yield and quality of these crops would be significantly reduced, leading to negative impacts on food production and availability.
Furthermore, bees and wasps contribute to maintaining biodiversity by supporting the reproduction of native plant species and facilitating the growth of various habitats. Their interactions with flowers and plants create a network of relationships that sustain ecosystems and provide food and shelter for other organisms.
Conservation Efforts and the Future
Given the critical role of bees and wasps in pollination, conservation efforts are crucial to ensure their long-term survival. The decline in bee populations, in particular, has raised concerns about the health of ecosystems and the sustainability of global food systems.
To support bee and wasp populations, it is important to protect their habitats, provide diverse and suitable forage resources, and reduce the use of pesticides that can harm these beneficial insects. Creating pollinator-friendly gardens and landscapes, planting native flowering plants, and avoiding the destruction of nesting sites can all contribute to their conservation.
By recognizing and appreciating the importance of bees and wasps in pollination, we can take action to protect and preserve these essential contributors to our ecosystems and agriculture. Coexistence with these insects involves not only addressing pest control and prevention but also promoting their conservation and creating a more sustainable future for both humans and the natural world.
Coexistence and Conservation of Bees and Wasps
Bees and wasps, despite their differences, both play crucial roles in our ecosystems. It is important to coexist with these insects and take measures to conserve their populations. Bees, in particular, are facing declining numbers, posing a threat to biodiversity and the pollination of agricultural crops. By promoting awareness and implementing conservation strategies, we can help ensure the survival of bees and wasps for future generations.
Conservation efforts for bees and wasps can be focused on providing suitable habitats and food sources. Planting bee-friendly flowers and plants in gardens and green spaces can attract and support these pollinators. Avoiding the use of harmful pesticides is also essential, as they can negatively impact both bees and wasps. Educating the public about the importance of bees and wasps and their role in pollination can further encourage conservation and coexistence.
In addition to conservation, it is vital to address any potential risks or concerns associated with bees and wasps. If a nest poses a threat to human safety or is causing damage to structures, professional pest control services should be sought. These experts can safely remove and relocate nests, minimizing harm to both humans and the insects.
Benefits of Coexistence and Conservation
The coexistence and conservation of bees and wasps offer several benefits. Bees are essential pollinators for a wide range of plants, including many food crops. Without bees, the production of fruits, vegetables, and nuts would be significantly affected. By preserving bee populations, we can help maintain healthy ecosystems and ensure food security.
Wasps, although often seen as pests, also have ecological value. They help control populations of pests such as caterpillars, flies, and spiders by preying on them or using them as food for their larvae. Their presence contributes to maintaining a balance in natural ecosystems.
| Benefits of Bees | Benefits of Wasps | |
|---|---|---|
| Pollination | Crucial for food production; supports biodiversity | Contributes to the control of pest populations; maintains ecological balance |
| Ecosystem Health | Ensures healthy ecosystems; supports plant diversity | Maintains a balance in natural ecosystems; controls pest populations |
| Food Security | Essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, and nuts | N/A |
The conservation of bees and wasps is not only crucial for their survival, but for the health of our planet as a whole. These insects play vital roles in pollination and maintaining ecological balance. By implementing conservation measures, we can protect these valuable creatures and the ecosystems they support.

Tips for Pest Control and Prevention
Pest control is essential when it comes to bees and wasps, especially if they pose a threat or risk to homes and businesses. Here are some tips for effective pest control and prevention:
Identifying the Problem
Firstly, it’s important to correctly identify whether you are dealing with bees or wasps. This will help determine the best course of action for removal and prevention. Bees are generally less aggressive and play a crucial role in pollination, so conservation efforts should be considered. Wasps, on the other hand, can be more aggressive and may require removal if they pose a risk to individuals.
Sealing Entry Points
Preventing bees and wasps from entering your property is key to avoiding infestations. Seal any cracks or openings in structures, including gaps around windows, doors, and utility lines. This will help keep these insects out and minimize the potential for nesting.
Removing Attractants
Bees and wasps are attracted to food and garbage, so it’s important to properly dispose of these items. Keep outdoor trash cans tightly sealed and regularly clean up any spills or food remnants. Additionally, avoid leaving sugary drinks or food uncovered, as this can attract these insects.
Professional Pest Control Services
If you have a significant infestation or are dealing with aggressive wasps, it’s best to seek professional pest control services. These experts have the knowledge, tools, and experience to safely remove nests and mitigate the risks associated with bees and wasps. They can also provide advice on long-term prevention strategies to minimize future infestations.
By following these tips for pest control and prevention, you can effectively manage and minimize the presence of bees and wasps on your property. Remember to always prioritize safety and conservation efforts when dealing with these important pollinators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between carpenter bees and wasps is essential for effective pest control and conservation efforts. While both play a role in pollination, carpenter bees should be conserved due to their declining populations and importance in the ecosystem. On the other hand, wasps can be more aggressive and may require removal if they pose a threat to homes or businesses.
Coexistence with bees and wasps is possible through proper pest control measures and prevention strategies. Regular inspections, sealing cracks, removing potential nesting sites, and proper waste management can help prevent infestations. By ensuring the conservation of their habitats and planting bee-friendly flowers, we can support the long-term survival of these important pollinators.
Overall, finding a balance between pest control, pollination, and the coexistence of bees and wasps is crucial. Through education and awareness, we can promote a healthier ecosystem and sustainable future where these insects can thrive alongside human communities.
FAQ
How can I tell the difference between bees and wasps?
Bees have rounder bodies, visible hair, flat hairy legs, and barbed stingers. Wasps have narrower bodies, invisible hair, cylindrical hairless legs, and smooth stingers.
Are wasps more aggressive than bees?
Yes, wasps are typically more aggressive and more likely to attack when threatened.
How can I identify different types of wasps?
Common types of wasps include hornets, mud daubers, paper wasps, and yellow jackets. Each has distinct characteristics and nesting habits.
What are some common types of bees?
Common types of bees include bumblebees, carpenter bees, honey bees, mining bees, sweat bees, and mason bees. Each has unique physical features and behaviors.
Do bees and wasps play a role in pollination?
Yes, both bees and wasps are important pollinators, helping plants reproduce and produce fruits and seeds.
How can I prevent bee and wasp infestations?
To prevent infestations, seal cracks and openings in structures, remove potential nesting sites, and properly dispose of food and garbage.
How do I safely remove bees and wasps?
It is best to seek professional help to safely remove and relocate nests. DIY methods may work for smaller infestations, but larger nests should be handled by professionals.
What should I do if I get stung by a bee or wasp?
If stung, remove the stinger if present, clean the area, apply ice to reduce swelling, and seek medical attention if experiencing severe allergic reactions.
Why is the conservation of bees important?
Bees are vital for biodiversity and ecosystem health. Their declining populations have a significant impact on the environment and agricultural crops.
How can I coexist with bees and wasps?
Coexistence can be achieved through proper pest control, prevention strategies, and the conservation of their habitats.