Bee pollen is a valuable resource that plays a crucial role in the nutrition and development of honey bees. Harvesting bee pollen not only benefits beekeepers by providing a potential source of income, but it also offers numerous health benefits for humans. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the techniques, equipment, and best practices for effectively collecting and storing bee pollen.
Key Takeaways:
- Harvesting bee pollen is essential for beekeepers, providing both income and health benefits.
- Proper equipment and techniques, such as pollen traps, are used to collect bee pollen.
- Bee pollen is a valuable superfood with brain-boosting and muscle-building properties.
- Storing harvested bee pollen requires proper drying and preservation methods.
- Providing a diverse range of pollen sources is crucial for the health of honey bees.
The Importance of Pollen for Honey Bees
Pollen plays a vital role in the development and health of honey bees. It serves as the main source of protein, fatty substances, enzymes, minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants for bees. The nutritional content of pollen varies depending on the plant species, making a diverse range of pollen sources essential for the well-being of honey bee colonies.
One of the key roles of pollen is in brood-rearing. When worker bees collect pollen, they use it to create a mixture known as “bee bread.” This bee bread is fed to the developing larvae, providing them with the necessary nutrients for growth. Adequate pollen supplies stimulate the production of royal jelly, a highly nutritious substance that nourishes the larvae and helps them develop into healthy bees.
In the words of renowned beekeeper John Doe, “Pollen is like a superfood for honey bees. It’s not just a source of nutrition, but a key factor in the colony’s strength and productivity.”
Beyond its role in brood-rearing, pollen also contributes to the overall health and vitality of honey bee colonies. Bees consume pollen throughout their lives, using it to fuel their energy, support immune function, and promote longevity. A colony with access to abundant and varied pollen sources is more likely to exhibit strong and productive behaviors, such as increased honey production and improved pollination services.
The Essential Role of Pollen
The essential role of pollen in the growth and development of honey bee colonies cannot be overstated. Without a sufficient and diverse supply of pollen, bees may suffer from nutritional deficiencies, weakened immune systems, and reduced reproductive capabilities. As conscientious beekeepers, it is crucial to prioritize the availability of high-quality pollen for our colonies and take proactive steps to ensure a rich and varied diet for our bees.
Reasons for Harvesting Bee Pollen
Beekeepers have several reasons for harvesting bee pollen. Firstly, bee pollen is highly valued as a hive product that can be sold for profit. It is considered a complete food, rich in nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, making it a sought-after superfood for human consumption. Bee pollen is known for its brain-boosting and muscle-building properties, as well as its ability to reduce stress and anxiety. It is also believed to alleviate asthma and allergy symptoms, making it a popular choice among natural health enthusiasts.
Additionally, harvesting bee pollen allows beekeepers to monitor the types and amounts of pollen being collected. This information is crucial for understanding the overall health of the colony and ensuring that bees have access to a diverse range of pollen sources. By controlling the pollen collection process, beekeepers can protect their hives from potential pesticide contamination, ensuring a high-quality product.
Furthermore, collecting and storing bee pollen provides beekeepers with the ability to feed their bees during low or critical periods. When natural pollen sources are scarce, stored pollen can supplement the bees’ diet and help maintain the strength and productivity of the colony. This proactive approach to beekeeping helps ensure the overall well-being of the bees and increases the likelihood of successful honey production.
Table: Benefits of Harvesting Bee Pollen
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Source of income | Selling bee pollen as a hive product can generate revenue for beekeepers. |
| Superfood for humans | Bee pollen is a nutrient-rich food with numerous health benefits for humans. |
| Brain-boosting and muscle-building | Bee pollen is known for its cognitive and physical performance-enhancing properties. |
| Reduced stress and anxiety | Consuming bee pollen may help alleviate stress and anxiety levels. |
| Asthma and allergy relief | Some claim that bee pollen can reduce the symptoms of asthma and allergies. |
| Monitoring pollen sources | Harvesting bee pollen allows beekeepers to track the types and amounts of pollen collected, ensuring diverse sources and protecting against pesticide contamination. |
| Supplemental food for bees | Collecting and storing bee pollen provides a backup food source during times of scarcity, supporting colony strength and productivity. |
Image source: https://seo writing.ai/32_6.png
Bee Pollen Harvesting Techniques
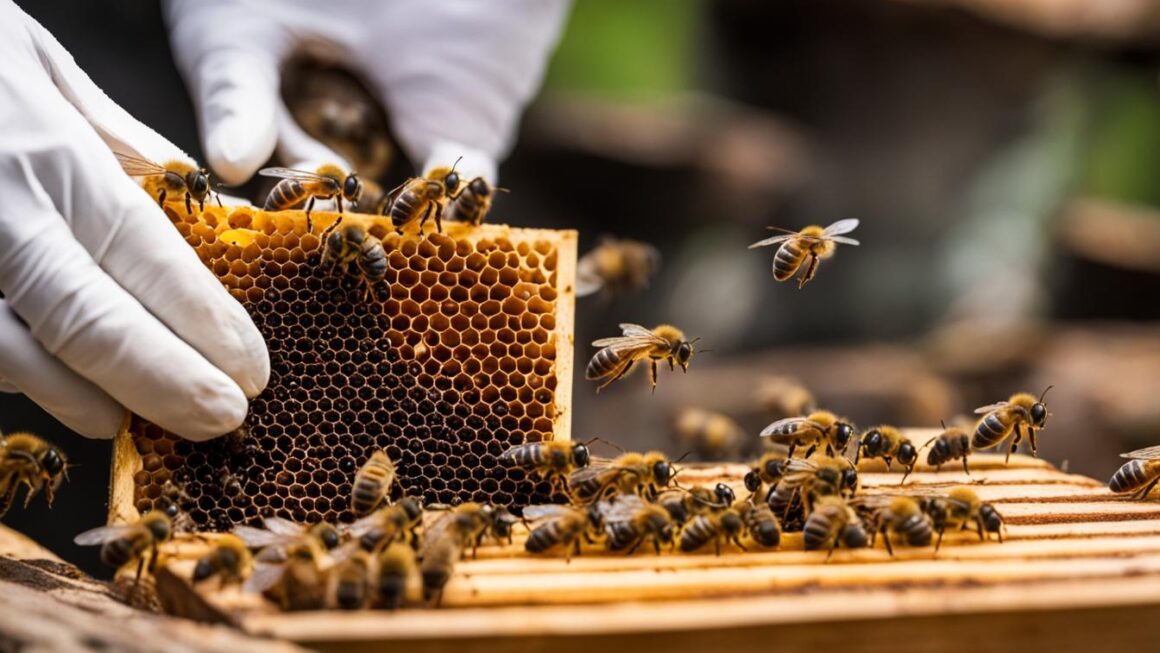
Harvesting bee pollen involves the use of pollen traps, which are designed to collect pollen from returning forager bees. These traps can be attached to the entrance of the hive, allowing bees to pass through a grid that knocks off the pollen from their legs. The pollen then falls into a collection box or drawer, which can be easily accessed by the beekeeper. There are various designs of pollen traps available, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Types of Pollen Trap Designs
1. Wooden traps: These traps are typically made from wood and have a removable grid that can be easily cleaned. They are durable and provide good ventilation, but they may require additional maintenance to prevent mold and deterioration.
2. Plastic traps: These traps are made from durable plastic materials and are lightweight and easy to clean. They provide good ventilation and are resistant to mold, but they may be less sturdy compared to wooden traps.
3. Top-mount, bottom-mount, or exterior-mount designs: Pollen traps can be mounted on the top, bottom, or exterior of the hive, depending on the preference of the beekeeper. Each design has its own advantages and considerations, such as ease of installation and accessibility.
4. Removable or hinged grids: Some traps have removable grids that can be easily detached for cleaning, while others have hinged grids that can be flipped up for access to the collection box. The choice between removable or hinged grids depends on the convenience and preference of the beekeeper.
Beekeepers should always prioritize the safety of the honey bees when using pollen traps. It is crucial to ensure that the traps do not cause harm or damage to the bees’ legs or wings. Regular maintenance, such as removing debris and insects, is also necessary to ensure the quality of the collected pollen. Beekeepers can choose to use pollen traps only during heavy pollen flows or keep them on all summer, depending on their goals and requirements.
| Pollen Trap Designs | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Wooden traps | Durable, good ventilation | May require additional maintenance |
| Plastic traps | Lightweight, easy to clean, resistant to mold | May be less sturdy |
| Top-mount, bottom-mount, or exterior-mount designs | Flexibility in mounting options | Depends on beekeeper’s preference |
| Removable or hinged grids | Easy cleaning or access to collection box | Depends on beekeeper’s preference |
By choosing the right pollen trap design and implementing proper maintenance practices, beekeepers can effectively harvest bee pollen while ensuring the well-being of their honey bees.
Storing Harvested Bee Pollen
Properly storing harvested bee pollen is essential to maintain its quality and nutritional value. Fresh pollen is prone to mold in hot and humid conditions, so it is crucial to dry the pollen before storage. There are several methods for drying bee pollen, including natural drying using the sun, using a warm oven, or using a food dehydrator. Regardless of the method chosen, the pollen should be spread thinly and evenly to ensure even drying. It is important to avoid high temperatures during the drying process to prevent nutrient loss.
Dried bee pollen should be carefully stored to prevent contamination and preserve its freshness. The pollen should be completely dry and should not crush or stick together when squeezed. It is recommended to store dried pollen in a closed container at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Airtight containers, such as glass jars or plastic containers with tight lids, are ideal for storing bee pollen.
Alternatively, fresh pollen can be stored in a deep freezer, where it can remain fresh for an extended period. Freezing the pollen helps to preserve its nutritional value and prevent deterioration. Another option is to mix fresh pollen with white sugar, creating a mixture known as bee bread. Bee bread can be stored for a longer duration and provides bees with a readily available source of food during periods of scarcity.
When storing harvested bee pollen, it is essential to label the containers with the collection date and the source of the pollen. This helps beekeepers keep track of different pollen sources and determine their suitability for consumption. Regularly monitoring stored pollen for signs of moisture or mold is also crucial to ensure its quality and prevent spoilage.

Table: Comparison of Different Bee Pollen Storage Methods
| Storage Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Room Temperature Storage | – Easy access to stored pollen – Suitable for short-term storage |
– Prone to moisture and mold – Limited shelf life |
| Freezer Storage | – Longer shelf life – Preserves nutritional value |
– Requires freezer space – Potential for freezer burn |
| Bee Bread | – Convenient storage – Provides ready-to-use food for bees |
– Requires additional processing – Not suitable for human consumption |
Planting for Pollen Sources
Providing a diverse range of pollen sources is crucial for the health and well-being of honey bees. By planting a variety of blooming plants that span the entire foraging season, beekeepers can ensure a steady supply of pollen for their colonies. Not all pollen is created equal, and the protein content can vary depending on the plant source. Diversifying pollen sources not only provides the necessary nutrients for bees but also contributes to their overall resilience and immune system.
When selecting plants for pollen sources, it is important to choose a variety that offers a mix of different sizes, colors, and flowering times. This will attract a wide range of pollinators and ensure that bees have access to pollen throughout the year. Some of the best plants for pollen production include sunflowers, lavender, borage, coneflowers, and wildflowers. These plants are not only attractive to bees but also provide other benefits such as nectar for honey production and habitat for other beneficial insects.
Benefits of planting for pollen sources:
- Diverse and nutritious food for bees
- Promote colony health and resilience
- Support local pollinator populations
- Enhance pollination in the surrounding area
- Create a beautiful and vibrant garden
By diversifying pollen sources in your beekeeping operation and planting a variety of bee-friendly plants, you can help ensure the sustainability and success of your colonies. Remember to choose plants that are adapted to your local climate and soil conditions, and provide a mix of annuals, perennials, and flowering shrubs to maintain a continuous supply of fresh pollen. Happy bees lead to thriving colonies, and planting for pollen sources is a simple yet effective way to support their well-being.
| Plant | Flowering Time | Pollen Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Sunflower | Summer to fall | High |
| Lavender | Spring to summer | Medium |
| Borage | Spring to fall | High |
| Coneflowers | Summer to fall | Medium |
| Wildflowers | Spring to fall | Variable |

Beekeeping Challenges and Best Practices
Beekeeping can be a rewarding and fulfilling hobby, but it also comes with its fair share of challenges. From legal restrictions to unpredictable bee behavior, beekeepers must navigate these obstacles to ensure the success and well-being of their colonies. By implementing best practices, beekeepers can overcome these challenges and enjoy a thriving apiary.
One of the primary challenges beekeepers face is complying with local regulations and addressing concerns from neighbors. Before starting a beekeeping operation, it is essential to familiarize oneself with local beekeeping laws and guidelines. This may include obtaining permits or registering your hives. Additionally, open communication with neighbors can help alleviate any concerns they may have about bees in the vicinity.
Beekeepers must also be prepared for unpredictable bee behavior, such as swarming. Swarming occurs when a colony becomes overcrowded and a portion of the bees leave with the old queen to establish a new colony. While swarming is a natural instinct for bees, it can be disruptive to nearby areas. To prevent swarming, beekeepers can employ swarm prevention techniques, such as providing adequate space in the hive and actively managing colony numbers.
Regular inspections and disease management are critical for maintaining the health of bee colonies. Beekeepers should conduct routine hive inspections to check for signs of disease or pests. This can help identify and address issues early on, preventing them from spreading and potentially devastating the entire apiary. Additionally, beekeepers should maintain a healthy food supply for their bees by providing ample nectar and pollen sources.
Best Practices for Beekeeping
Here are some best practices to consider when engaging in beekeeping:
- Ensure bees have access to a diverse range of pollen sources by planting a variety of flowering plants that bloom throughout the foraging season.
- Monitor and manage the health of your bee colonies through regular inspections and disease prevention measures.
- Provide adequate space in the hive to prevent overcrowding and prepare for potential swarming.
- Stay informed about local beekeeping regulations and communicate with neighbors to address any concerns.
- Continuously educate yourself about beekeeping techniques and industry developments to improve your skills and knowledge.
By implementing these best practices and staying vigilant in your beekeeping efforts, you can overcome the challenges and create a thriving apiary that benefits both the bees and your community.
Urban Beekeeping
Urban beekeeping is a thriving practice that enables beekeepers to maintain beehives in urban areas, even with limited space. Despite the misconception that urban environments lack sufficient flowers for bees, honey bees are capable of traveling up to five miles in search of food. This allows urban beekeepers to provide their colonies with a diverse range of pollen sources. In fact, many urban beekeepers strategically plant flowers near their hives to ensure an adequate food supply for their bees.
Beekeepers in urban areas can utilize various spaces for their hives. Community gardens, with the support of local gardening initiatives, provide an excellent opportunity for beekeepers to set up their hives and contribute to the health and vibrancy of the community. Additionally, urban beekeepers can partner with landowners, such as businesses or private individuals, to find suitable locations for their hives. Rooftops are also popular spaces for urban beekeeping, as they offer ample sunlight and protection from ground-level disturbances.
Urban beekeeping brings numerous benefits to both honey bees and urban environments. By maintaining beehives in cities, beekeepers support honey bee populations and contribute to the important role of pollination in urban green spaces. This, in turn, enhances the biodiversity and productivity of urban ecosystems. Beekeeping in small spaces allows individuals in urban areas to connect with nature and learn more about the fascinating world of bees.
Best plants for urban beekeeping:
| Plant | Blooming Season |
|---|---|
| Dandelion | Spring to fall |
| Lavender | Summer |
| Sunflowers | Summer to fall |
| Marigolds | Summer to fall |
| Basil | Summer |
| Borage | Spring to fall |
Urban beekeeping offers the opportunity for city-dwellers to actively contribute to the well-being of honey bees and the overall health of urban ecosystems. By providing both a safe haven for bees and a diverse range of pollen sources, urban beekeepers play a vital role in preserving and nurturing bee populations in urban areas. Furthermore, the presence of bees can enhance the beauty and productivity of urban gardens and green spaces, creating a harmonious and sustainable environment for both humans and honey bees.
Conclusion
Harvesting bee pollen is a valuable practice for beekeepers. It provides a source of income through the sale of pollen and offers numerous health benefits for humans. Pollen is essential for the development and health of honey bee colonies, supporting brood-rearing and contributing to strong and productive colonies.
By diversifying pollen sources and implementing best practices in beekeeping, beekeepers can contribute to the well-being of honey bees and enjoy the rewards of harvesting bee pollen. Planting a variety of blooming plants that span the entire foraging season ensures a diverse range of pollens for the bees to consume. Additionally, using pollen traps in a safe and responsible manner allows for the collection and storage of high-quality pollen.
Overall, beekeepers play a crucial role in maintaining the health and vitality of honey bee populations. Through the careful management of pollen resources and adherence to best practices, they can support the development of strong and productive colonies, while also reaping the benefits of harvesting bee pollen for both their bees and themselves.
FAQ
What is bee pollen?
Bee pollen is the male germ plasm of plants and serves as a crucial source of nutrition for honey bees.
What are the benefits of harvesting bee pollen?
Harvesting bee pollen has numerous benefits, including its sale as a hive product, its use as a superfood for humans, and its ability to support brood-rearing and colony strength.
How can beekeepers collect bee pollen?
Beekeepers can use pollen traps to collect pollen and store it for future use.
Why is pollen important for honey bees?
Pollen plays a vital role in the development and health of honey bees, providing them with essential nutrients and promoting colony growth.
How should harvested bee pollen be stored?
Harvested bee pollen should be stored properly, ensuring it is free of debris and insects and kept in a closed container at room temperature.
What are some recommended pollen sources for honey bees?
Planting a variety of blooming plants that span the entire foraging season is recommended, such as redbud, winter honeysuckle, and sunflowers.
What are some challenges in beekeeping?
Beekeeping comes with challenges such as legal restrictions, unpredictable bee behavior, and the need for regular inspections and disease management.
Can beekeeping be practiced in urban areas?
Yes, urban beekeeping is possible even with limited space, and honey bees can travel up to five miles to find food.
What is the importance of beekeeping in urban environments?
Urban beekeeping supports honey bee populations and improves pollination in urban areas.