Carpenter bees, a species of solitary insects, play a vital role in the ecosystem. Understanding the differences between male and female carpenter bees is essential for comprehending their unique characteristics and behaviors. In this comparative study, we will explore the distinct roles and physical attributes of male and female carpenter bees. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of these industrious insects.
Key Takeaways:
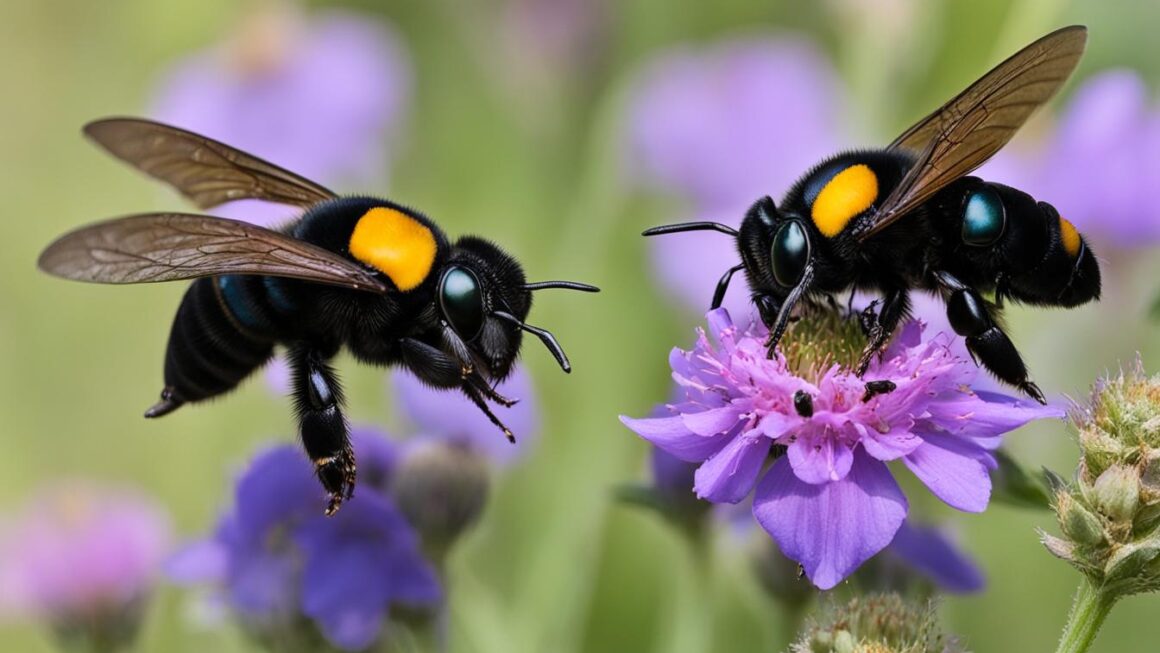
- Male and female carpenter bees have different markings on their heads: small white markings for males and pure black heads for females.
- Male carpenter bees are unable to sting, while female carpenter bees possess a painful sting.
- Both male and female carpenter bees contribute to the survival of the species through nest construction and reproduction.
- Male carpenter bees defend their territory and protect the females, relying on intimidation tactics rather than stinging.
- Female carpenter bees bore tunnels in wood for their nests using their powerful jaws.
Physical Characteristics of Male Carpenter Bees
Male carpenter bees share many physical characteristics with females, but there are certain features that distinguish them. These bees have large, black bodies with a velvety appearance. They are slightly smaller in size compared to their female counterparts.
The most notable characteristic of male carpenter bees is the presence of small white markings on their heads. These markings, often shaped like a “W” or an “X,” are unique to male bees and can be used to identify them. Additionally, male carpenter bees do not possess stingers, unlike the females.
While their overall physical appearance may seem similar to females, the distinctive white markings on their heads serve as a clear identifier for male carpenter bees. Their lack of stingers also sets them apart, allowing them to focus on protecting the females and defending their territory.
| Physical Characteristics | Male Carpenter Bees | Female Carpenter Bees |
|---|---|---|
| Body Color | Black | Black |
| Head Markings | Small white markings | Pure black |
| Size | Slightly smaller | Slightly larger |
| Stinger | Absent | Present |
Understanding the physical traits of male carpenter bees can be helpful in distinguishing them from female carpenter bees. The unique white markings on their heads and their lack of stingers provide key identifiers for male bees.
Physical Characteristics of Female Carpenter Bees
Female carpenter bees exhibit distinct physical characteristics that set them apart from their male counterparts. These traits play a crucial role in their role as nest builders and egg-layers. Understanding the physical characteristics of female carpenter bees can aid in their identification and provide valuable insights into their behavior.
Body Size and Coloration
Female carpenter bees are generally larger in size compared to males. Their bodies can reach lengths of up to one inch, while males are slightly smaller. The larger body size allows females to accommodate the eggs they carry and provide ample space for nesting materials.
When it comes to coloration, female carpenter bees have black bodies with pure black heads. This stark contrast makes them easily distinguishable from their male counterparts, who have small white markings on their heads. The black head of female carpenter bees serves as a visual cue, indicating their ability to deliver a painful sting if threatened.
Jaws and Nest Construction
Female carpenter bees possess powerful jaws that enable them to bore tunnels in wood for nest construction. These jaws allow them to create intricate and durable nests, protecting their eggs from predators and the elements. The nest construction process involves chewing through wood, creating channels for their offspring to develop and thrive.
| Physical Characteristics | Female Carpenter Bees | Male Carpenter Bees |
|---|---|---|
| Body Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Head Coloration | Pure black | Small white markings |
| Jaws | Powerful for tunneling in wood | N/A |
| Sting | Present | Absent |
Table: Physical characteristics comparison between female and male carpenter bees.
As female carpenter bees fulfill their vital roles in nest construction and egg-laying, their physical characteristics allow them to excel in these tasks. The powerful jaws and larger sizes enable them to create and protect their nests effectively, ensuring the survival of future generations of carpenter bees.
Behavior of Male Carpenter Bees
Male carpenter bees exhibit distinct behaviors that revolve around protecting the female carpenter bees and defending their territory. They are not aggressive by nature but can become defensive when their territory is threatened.
One prominent behavior of male carpenter bees is their tendency to dive-bomb intruders, including humans, as a scare tactic. This behavior is often seen when someone approaches their nesting areas or tries to interfere with the female carpenter bees. It is important to note that while male carpenter bees may appear intimidating, they cannot sting.
Instead of relying on stingers, male carpenter bees utilize their larger size as a defense mechanism. They will fly close to intruders and create a buzzing sound, which is usually enough to deter any potential threats. Male carpenter bees are generally docile and will only exhibit defensive behavior when provoked or if they sense a direct threat to the female carpenter bees or their territory.
Table: Comparison of Male and Female Carpenter Bee Behavior
| Male Carpenter Bees | Female Carpenter Bees | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Protecting the female carpenter bees and defending their territory | Nest construction and egg-laying |
| Stinging Ability | Cannot sting | Can deliver a painful sting if provoked |
| Defense Mechanism | Intimidation through size and buzzing | Stinging when threatened |
| Aggression | Not aggressive unless provoked | Less aggressive than males, prioritize nest protection |
Understanding the behavior of male carpenter bees can provide valuable insights into their role within the carpenter bee community. By respecting their territory and avoiding unnecessary interference, we can coexist with these important pollinators while appreciating their unique behaviors.
Behavior of Female Carpenter Bees
Female carpenter bees exhibit specific behaviors that are essential for their survival and the continuation of their species. These behaviors primarily revolve around nest construction and egg-laying, as well as protecting their nests from potential threats. Understanding the behavior of female carpenter bees can provide valuable insights into their fascinating world.
One of the key behaviors of female carpenter bees is their adeptness in nest construction. These industrious bees use their powerful jaws to bore tunnels in wood, creating suitable environments for their eggs. By excavating these tunnels, female carpenter bees ensure that their offspring have a safe place to develop and grow. This behavior is crucial for the survival and propagation of the species.
Another important behavior of female carpenter bees is their dedication to protecting their nests. When a female carpenter bee senses a potential threat, she will become defensive and may deliver a painful sting if provoked. This protective behavior is driven by the instinct to safeguard her eggs and ensure their successful development. While female carpenter bees are generally less aggressive than their male counterparts, they prioritize the protection of their offspring and nest.
Behavior of Female Carpenter Bees in Summary:
- Proficient in nest construction, using powerful jaws to bore tunnels in wood
- Dedicated to protecting their nests and eggs through defensive measures
- Less aggressive than male carpenter bees but can deliver a painful sting if provoked
Table: Comparison of Behavior Between Male and Female Carpenter Bees
| Male Carpenter Bees | Female Carpenter Bees | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Protect the female and defend territory | Construct nests and lay eggs |
| Physical Characteristics | Larger bodies with white markings on the head | Larger bodies with pure black heads |
| Stinging | No stinger | Can deliver a painful sting |
| Aggression | Defensive and protective | Less aggressive but prioritizes nest protection |
By understanding the behavior of female carpenter bees, we gain an appreciation for the intricate and vital role they play in their ecosystems. Their dedication to nest construction, egg-laying, and nest protection ensures the survival and prosperity of their species. As important pollinators, female carpenter bees contribute to the health and biodiversity of our natural environments.
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Carpenter Bees
Carpenter bees reproduce through a mating process between a male and female bee. After emerging from hibernation in the spring, male and female carpenter bees search for mates. Once they find each other, the female carpenter bee begins the process of nest construction.
The female carpenter bee builds her nest by using her powerful jaws to bore tunnels into wood. These tunnels serve as chambers in which she will lay her eggs. Inside each chamber, the female carpenter bee places a supply of pollen for the developing larvae to feed on.
After the nest construction is complete, the female carpenter bee lays her eggs inside the chambers. The eggs hatch, and the larvae begin to feed on the stored pollen. Over time, the larvae grow and develop into adult carpenter bees.
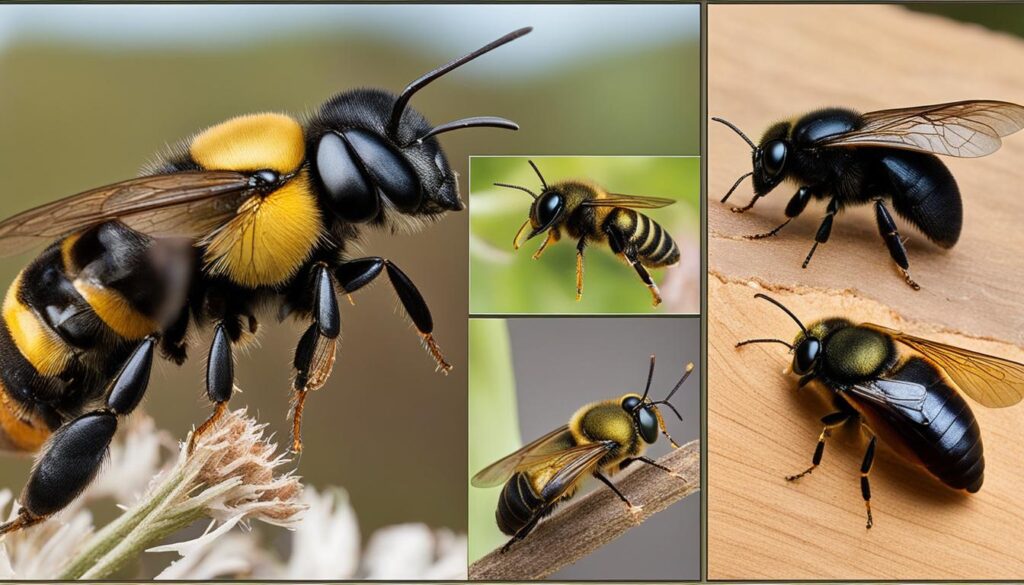

Table: Carpenter Bee Life Cycle
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Egg | The female carpenter bee lays her eggs inside the nest chamber. |
| Larva | The larvae hatch from the eggs and feed on the stored pollen. |
| Pupa | The larva spins a cocoon and undergoes metamorphosis inside the chamber. |
| Adult | The fully developed adult carpenter bee emerges from the chamber and begins the cycle again. |
At the end of the season, both the male and female carpenter bees die. The next generation of carpenter bees will emerge in the following spring, continuing the life cycle. Understanding the reproduction and life cycle of carpenter bees is essential for effectively managing their populations and coexisting with these important pollinators.
Impact of Carpenter Bees on the Environment
Carpenter bees play a vital role in the environment as pollinators. They visit flowers to collect pollen, transferring it from one flower to another, which aids in plant reproduction. This process is crucial for the growth and diversity of plant species. Carpenter bees, with their large bodies, are efficient pollinators, ensuring the survival of numerous plants and the maintenance of healthy ecosystems.
However, the wood-boring behavior of carpenter bees can have an impact on wooden structures. These bees create tunnels in wood for their nests, which can weaken the structural integrity of buildings, decks, and other wooden objects. Over time, the accumulation of tunnels can lead to significant damage, requiring costly repairs.
To coexist with carpenter bees while minimizing their impact on wooden structures, several precautions can be taken. Applying protective coatings, such as paint or varnish, to exposed wood surfaces can act as a deterrent, as carpenter bees are less likely to bore into treated wood. Regular inspections and prompt repair of any existing damage can help prevent further deterioration. In some cases, professional pest control services may be necessary to address severe infestations.
| Impact of Carpenter Bees | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Carpenter bees are important pollinators. | Protective coatings on wooden surfaces can minimize nesting activities. |
| Their wood-boring behavior can cause damage to wooden structures. | Regular inspections and repairs can prevent further deterioration. |
| Accumulation of tunnels weakens the structural integrity of wood. | Professional pest control services may be necessary for severe infestations. |
Pollination and Preservation
It is important to strike a balance between preserving the ecological benefits of carpenter bees as pollinators and safeguarding the integrity of wooden structures. By implementing preventive measures and promptly addressing any issues, we can maintain a healthy environment while minimizing the impact of carpenter bees on our surroundings.
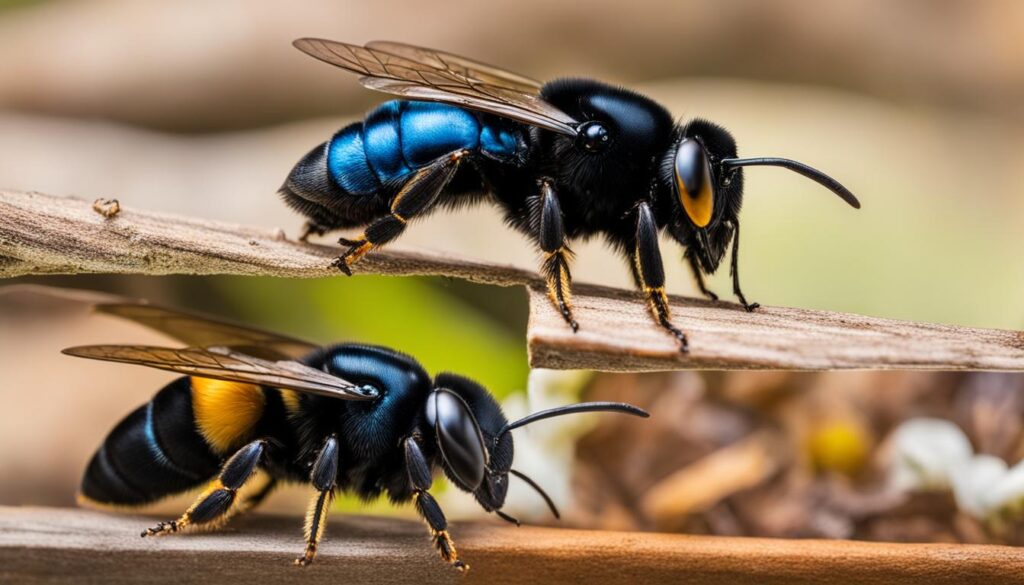

Similarities Between Male and Female Carpenter Bees
Male and female carpenter bees share several common traits, despite their distinct roles and physical differences. Both genders belong to the same species and are solitary insects. They are important pollinators, actively visiting flowers to collect pollen, which contributes to the reproduction of plants. Carpenter bees, regardless of gender, play a crucial role in maintaining the ecosystem’s biodiversity.
Another shared characteristic between male and female carpenter bees is their nesting habits. Both genders construct their nests by drilling tunnels into wood. These tunnels provide shelter and protection for their offspring. The carpenter bee tunnels can also benefit other species that may utilize them once the bees have moved on.
Male and female carpenter bees, although they have different roles, both contribute to the survival and reproduction of their species. Understanding their common traits and behaviors helps in appreciating their importance as pollinators and in fostering coexistence with these beneficial insects.
While male and female carpenter bees have their distinctive physical characteristics, such as the markings on their heads, their larger bodies, and the presence or absence of stingers, it is important to recognize their shared similarities. Appreciating these similarities can deepen our understanding of the carpenter bee species and inspire efforts to protect and preserve their habitats for the benefit of our ecosystem.
| Shared Traits | Male Carpenter Bees | Female Carpenter Bees |
|---|---|---|
| Species | Carpenter bee (Xylocopa) | Carpenter bee (Xylocopa) |
| Pollination | Actively visit flowers to collect pollen | Actively visit flowers to collect pollen |
| Nesting Habits | Construct tunnels in wood for nests | Construct tunnels in wood for nests |
Conclusion
Male and female carpenter bees have distinct roles and characteristics. The male carpenter bee’s primary job is to protect the female and defend their territory. They cannot sting and rely on intimidation tactics. Female carpenter bees, on the other hand, are responsible for nest construction and egg-laying. They possess stingers and can deliver a painful sting if provoked.
Understanding the differences between male and female carpenter bees is important in identifying and coexisting with these important pollinators. Male carpenter bees have small white markings on their heads, while females have pure black heads. It is also worth noting that female carpenter bees have larger bodies compared to males. Both genders contribute to the reproduction and survival of the species and are crucial pollinators during the spring season.
In summary, male vs female carpenter bees comparison highlights the specialized roles of each gender. Males protect and defend, while females construct nests and lay eggs. By appreciating these distinctions, we can foster a harmonious relationship with these valuable insects and continue to benefit from their crucial pollination services.
FAQ
What is the difference between male and female carpenter bees?
The key difference between male and female carpenter bees is the markings on their heads. Males have small white markings, while females have pure black heads. Males do not have stingers, while females can deliver a painful sting.
How can I differentiate male and female carpenter bees?
Male carpenter bees have small white markings on their heads, while female carpenter bees have pure black heads. Additionally, males are slightly smaller in size compared to females.
Are male carpenter bees aggressive?
Male carpenter bees are not aggressive unless provoked. Their main focus is protecting the female carpenter bees and defending their territory.
Can female carpenter bees sting?
Yes, female carpenter bees have stingers and can deliver a painful sting if their nest is disturbed.
What is the role of male carpenter bees?
Male carpenter bees primarily protect the female carpenter bees and defend their territory. They do not have stingers and rely on their large size for intimidation.
What is the role of female carpenter bees?
Female carpenter bees are responsible for nest construction and laying eggs. They also have powerful jaws that they use to bore tunnels in wood for their nests.
How do carpenter bees reproduce?
Carpenter bees reproduce through mating between a male and female bee. After mating, the female carpenter bee builds a nest, lays her eggs inside, and provides pollen for the larvae to feed on.
What impact do carpenter bees have on the environment?
Carpenter bees play a role in pollination as they visit flowers to collect pollen. However, their wood-boring behavior can cause damage to wooden structures.
What are the similarities between male and female carpenter bees?
Both male and female carpenter bees belong to the same species, have similar physical characteristics, and share the habit of building tunnels in wood for their nests.